Early Modern (1450 CE - 1800 CE)
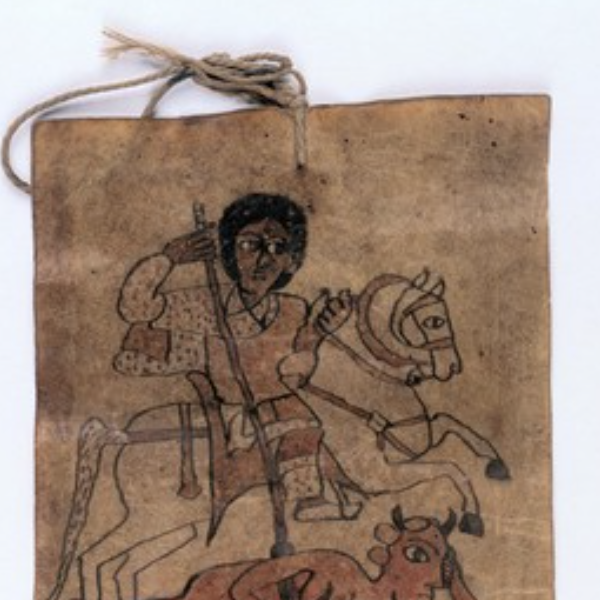

Ethiopian Healing Scrolls
Ethiopian healing scrolls are believed to eliminate sickness by ridding spirits and demons from an ill person. Originating sometime between the 1st and 8th century CE in the Axum empire, the scrolls are still used to this day, and still written in the Ge’ez script of the Axum empire.

Inca Miniature Tunic
This cotton and camelid hair tunic dates from the 14th-16th century CE in Peru, and was simply constructed from a rectangle of fabric, with a slit for the neck and open sides for the arms.
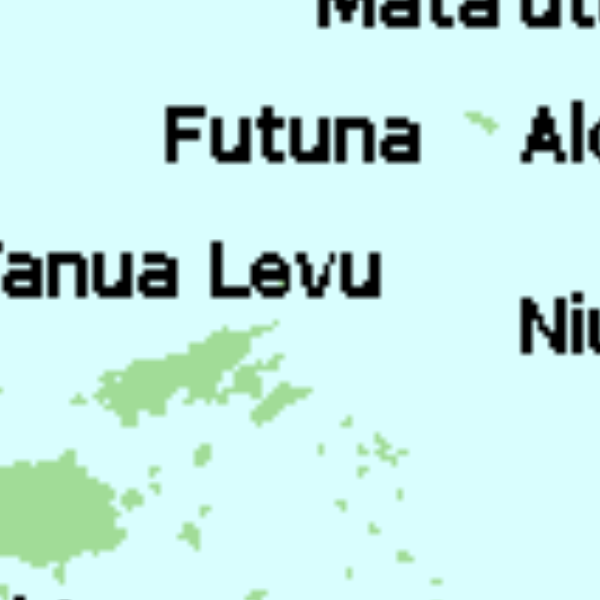
Tu'i Tonga Empire Map
The Tu’i Tonga Empire was an Oceanic maritime chiefdom centered on the island of Tongatapu, the main island of Tonga, and flourished between 1200-1500 CE.
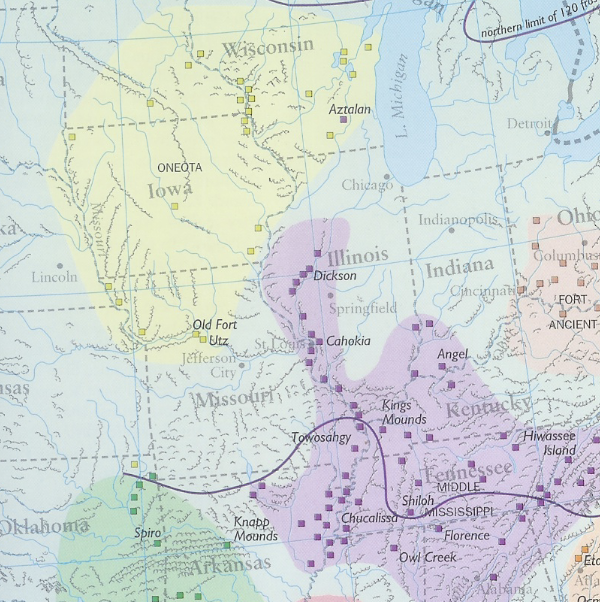
The Moundbuilders' Art: A Confluence of 'Ingenuity, Industry, and Elegance'
The amount of information and resources included in the exhibit are targeted and would likely not overwhelm a high school student. Alternatively, the site is full of resources that could be used separately, especially for younger students.
Te Paranihi, or Maori War Canoe
Te Paranihi is a 17-meter (55 feet) war canoe, or waka taua, from the Maori culture indigenous to New Zealand.
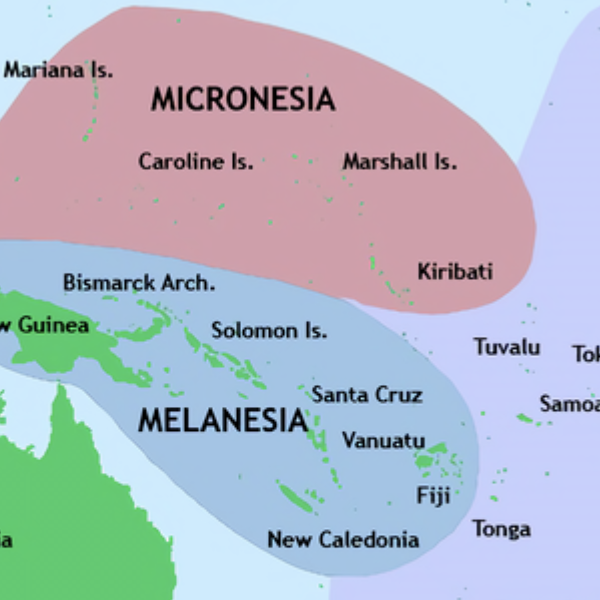
Pacific Culture Areas Map
This map illustrates the three dominant cultures in Oceania, Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia, and which islands occupy each region. This map successfully highlights the number of island nations/cultures and the overall size of Oceania.
Polynesian Oral Traditions
This collection compiled by Rawiri Taonui, a professor of Indigenous Studies, includes creation myths and stories about gods, the origin of humanity, and cultural heroes for several Polynesian cultures, such as Hawaii, Samoa, Tonga, Tahiti, and numerous others.
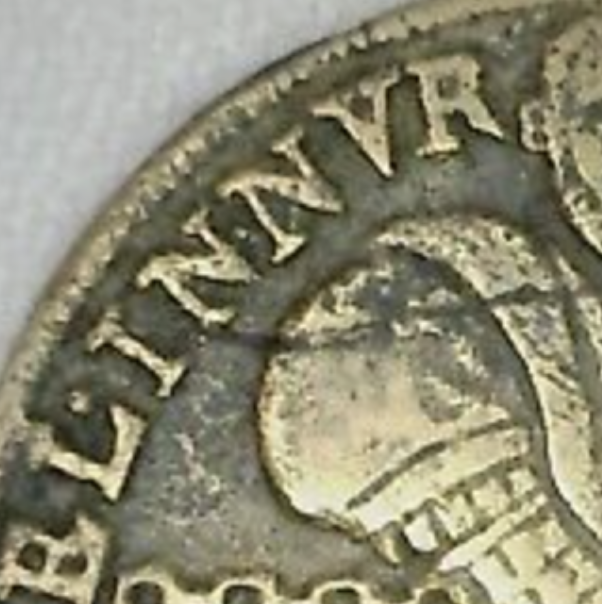

Early Modern Counter
An early modern counter of the "Reichenmaster" style, with one side showing a picture of a man using a counting board and the other side showing the alphabet. These counters were used in classrooms to teach students both to read and perform basic arithmetic.
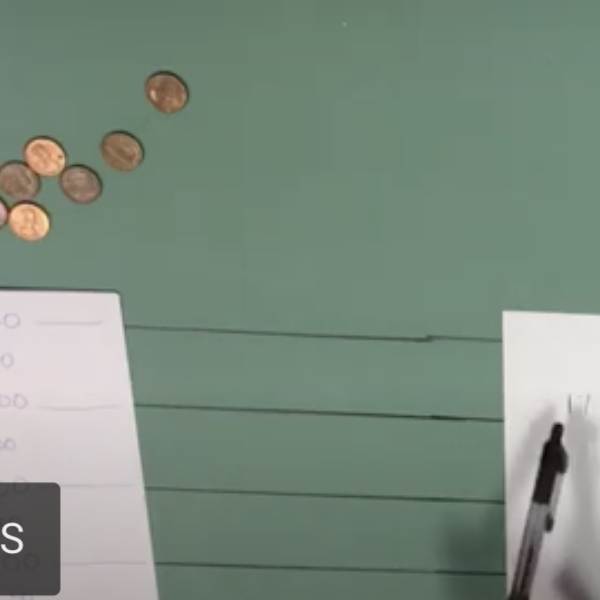

Division with an Early Modern Counting Board
Before the rise of literacy rates, counting boards such as the one featured in the video were the most common way to perform arithmetic. After pen-and-paper arithmetic replaced counting boards, Arabic numerals also became dominant throughout Europe.
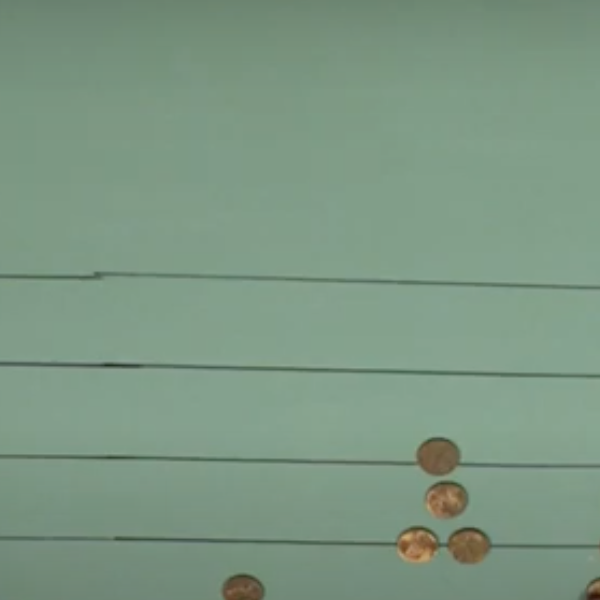

Multiplication with an Early Modern Counting Board
Before the rise of literacy rates, counting boards such as the one featured in the video were the most common way to perform arithmetic. After pen-and-paper arithmetic replaced counting boards, Arabic numerals also became dominant throughout Europe.