Politics
Maya Drinking Vessel with Seated Lord, 7th-8th century
This large ceramic vessel, made for drinking chocolate, shows a figure wearing a loincloth, necklace, and a large headdress that looks like the tail feathers of the quetzal bird.

Economic Declaration of Nonaligned Countries
This document is part of the economic declaration of the Fourth Nona

"The Problems of Third World Development"
The text is an excerpt from the 1974 Houari Boumédiène’s speech to t

Short Teaching Module: The Nonaligned Movement and Cold War Détente
Since the early Cold War, neutral and nonaligned countries sought to

Primer: Borderlands History
Borderlands history studies the making and crossing of borders. While the term “borderlands” has no fixed definition, it can refer to spaces of encounter between different peoples and political entities.
Policy Statement of the Federal Military Government Issued by Nigerian Embassies Abroad, 1966
In 1966, Nigeria was only a few years removed from colonial status. Nigeria as a unified political and economic entity had only been established in 1914 with the merger of the very different regions of northern and southern Nigeria.
Excerpt from the Kellogg-Briand Pact, 1928
Also known as the Pact of Paris, the Kellogg-Briand Pact of 1928 was an international agreement sponsored by the United States and France aimed to eliminate war as a means of conflict resolution on the international playing field following World War I.
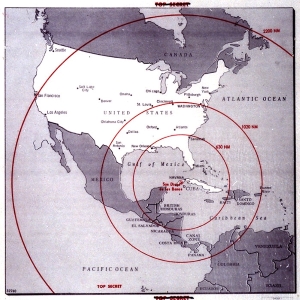
Map of the Range of Nuclear Missiles in Cuba, 1962
Marking one of the most dangerous periods of the Cold War, the Cuban Missile Crisis began on October 16, 1962, when U.S. national security advisors alerted President John F. Kennedy that a Soviet missile base was under construction in Cuba.
Analyzing Official Documents
Official documents produced by governments, supranational organizations, courts of law, and more are abundant in supply, but can be intimidating and confusing to approach. They are often filled with language that seems convoluted, emotionless, and highly technical.
