Government
Al-Umari’s Account of Mansa Musa’s Visit to Cairo
Mansa Musa was the leader of the Mali empire in the fourteenth century and reportedly the wealthiest person – allegedly ever. The empire covered modern-day Mali and parts of Guinea, Senegal, Mauritania, and the Gambia, and Mansa Musa expanded the territorial claim to include Gao and Timbuktu.

Poverty Point in Louisiana, United States
Poverty Point is a prehistoric earthenwork site featuring mounds, ridges, and a ceremonial plaza located in northeastern Louisiana, United States.

The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site is an archaeological site of a pre-Columbian Native American city located in southwestern Illinois, near St. Louis, Missouri.
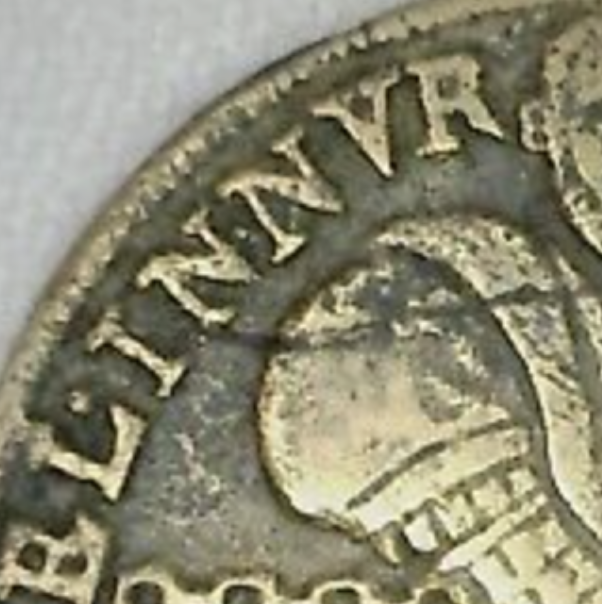

Early Modern Counter
An early modern counter of the "Reichenmaster" style, with one side showing a picture of a man using a counting board and the other side showing the alphabet. These counters were used in classrooms to teach students both to read and perform basic arithmetic.
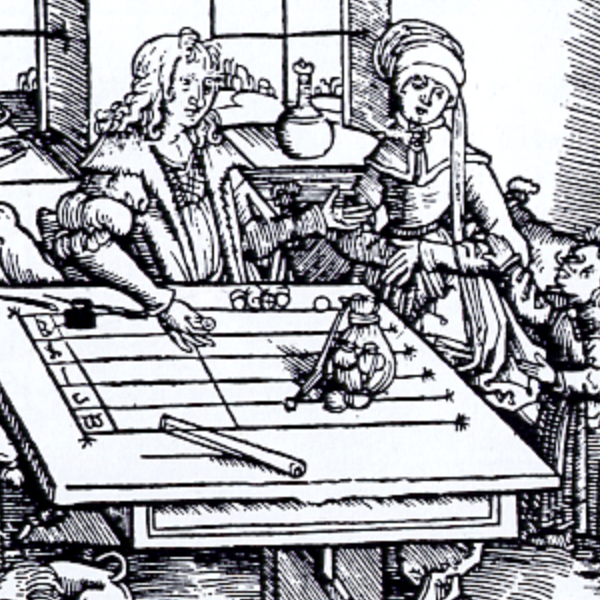

Engraving of a Rechentisch (Counting Board)
This image of an engraving depicts a man using a rechentisch, or counting board, the earliest known counting device and a precursor the abacus. The earliest known counting board is the Salamis Tablet, dating from 300 BCE, but may have been used more for gaming than for calculating.

History of Pre-Modern Math
Before the widespread adoption of Arabic numerals, medieval and early modern Europeans added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided using a type of abacus known as a counting board and only afterwards recorded the results of their ca
Economic Diplomacy in the Caribbean Since the Second World War
Economic affairs are an essential part of world history and, even more so, in contemporary times after World War II, when globalization processes with higher levels of interdependency and proximity among individuals and countries are increasingly observed.

OECS Treaty Publication Fragments
The OECS published in 1988 a booklet explaining the treaty that founded it (OECS 1988). A fragment is included in the photos here.
Transcript of the Treaty of Basseterre of 1981
To capture the diplomatic side of Caribbean economic history from the point of view of the governments, official documents describing economic policies, joint strategies, and related decision-making processes in the Caribbean

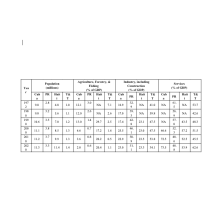
Popular World Development Indicators for Four Caribbean Countries
Raw numerical data may be pursued to track historical behavior through socioeconomic and demographic indicators.