Popular World Development Indicators for Four Caribbean Countries
Annotation
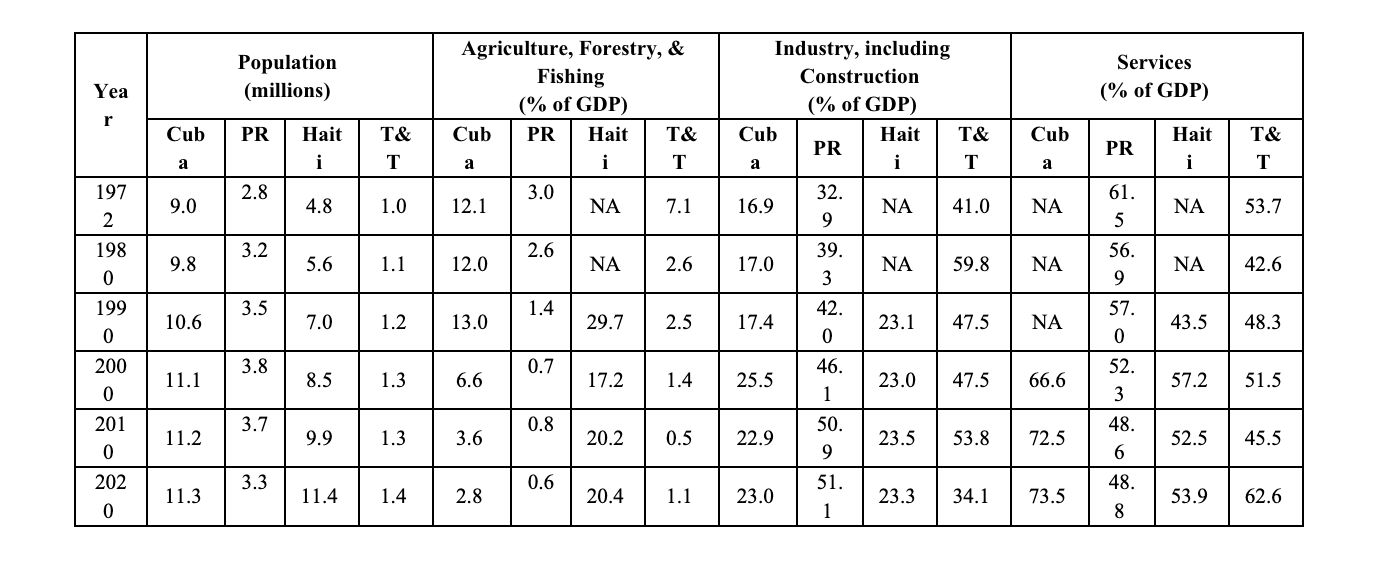
Raw numerical data may be pursued to track historical behavior through socioeconomic and demographic indicators. This data might be the basis to identify and understand socioeconomic challenges and potential solutions that should be addressed through economic diplomacy. This information might be useful to understand historical trends in specific products grown, produced, or manufactured (from bananas and sugar to hospitality and financial services); the evolution of specific economic activities; and indicators such as population, literacy rates, income per capita, or gross domestic product (GDP) as a measure of a country’s productivity.
As an example of this kind of data, the information in the table above was obtained from the World Bank databases for four Caribbean countries: Cuba, Puerto Rico, Haiti, and Trinidad & Tobago. They are country population measured in millions and the percentage of the country’s total production (GDP) for three economic activities: agriculture, industry, and services. The numbers are provided for about every ten years between 1972 and 2010.
Observations like the following may be uncovered by the numbers in the table:
-
The significantly higher rate of growth in Haitian population as compared to the other countries
-
The effect in the population of Puerto Rico of the multiple crises (government bankruptcy, hurricane recovery, earthquake recovery, pandemic impact) since 2006, also keeping in mind the unrestricted access of Puerto Rican migrants to the mainland US since the island (or archipelago) is part of the US political system as one of five associated states
-
The declining importance of agriculture in the Caribbean after being the main activity during the nineteenth century and the first part of the twentieth century, posing at the same time a challenge to food security
-
The definite importance of both industry and services in the economy today’s Caribbean societies
-
The higher development of industry in both Puerto Rico and Trinidad & Tobago when compared to Cuba and Haiti
-
The effect of the rapid growth of tourism-related activities in Cuba’s services sector
-
The effect in the Trinidad & Tobago’s industrial sector of the oil production booms during the decades of the 1970s and the 2000s (see the industry’s percentage of GDP in 1980 and 2010)
This source is part of the Economic Diplomacy in the Caribbean Since the Second World War teaching module.
Transcription
Year Population (millions) Agriculture, Forestry, & Fishing (% of GDP) Industry, including Construction (%) of GDP Services (% of GDP)
Cuba PR Haiti T&T Cuba PR Haiti T&T Cuba PR Haiti T&T Cuba PR Haiti T&T
1972 9.0 2.8 4.8 1.0 12.1 3.0 NA 7.1 16.9 32.9 NA 41.0 NA 61.5 NA 53.7
1980 9.8 3.2 5.6 1.1 12.0 2.6 NA 2.6 17.0 39.3 NA 59.9 NA 56.9 NA 42.6
1990 10.6 3.5 7.0 1.2 13.0 1.4 29.7 2.5 17.4 42.0 23.1 47.5 NA 57.0 43.5 48.3
2000 11.1 3.8 8.5 1.3 6.6 0.7 17.2 1.4 25.5 46.1 23.0 47.5 66.6 52.3 57.2 51.5
2010 11.2 3.7 9.9 1.3 3.6 0.8 20.2 0.5 22.9 50.9 23.5 53.8 72.5 48.6 52.5 45.5
2020 11.3 3.3 11.4 1.4 2.8 0.6 20.4 1.1 23.0 51.1 23.3 34.1 73.5 48.8 53.9 62.6
Credits
"Databank: World Development Indicators," The World Bank, https://databank.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.POP.TOTL/1ff4a498/Popular-Indicators#