Law
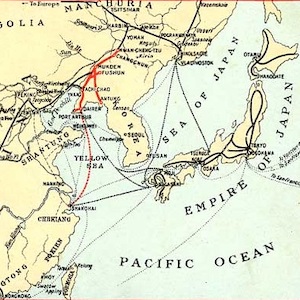
Southern Manchuria Railway (1906-1945)
The world’s earliest locomotive-operated railroads, short stretches transporting coal and ore locally from mines to factories and furnaces, were developed in Britain between 1800 and 1825.

Short Teaching Module: Shared Space, Shared Experiences: Transnational Water Management around the Great Lakes
World historians sometimes work within a single sub-field, such as migration history or gender history, but they can also bring sub-fields together, as their perspectives, methods, and subject matter cross boundaries.

Emmerton Letter, 1926
Between 1919 and 1935, citizens of the U.S. and Canada complained about industrial pollution from an American company called the Solvay Process Company (also called the Michigan Alkali Corporation), which dumped its wastes on Fighting Island, in the Detroit River.
Sikkim Photos (Kandell Collection)
This collection offers a peek into how people lived in the Kingdom of Sikkim, despite the kingdom and monarchy no longer existing in the same form today.Korean Rare Book Digital Collection
These collection's topics include history, politics, social life and values, education, biology and more from the pre-modern Korean perspective.
Indigenous Law Web Archive
The Indigenous Law Web Archive is an archive of documents concerning the laws and practices of Indigenous nations of the US, which have their own sovereign governments.Piracy Trials
As the title suggests, the collection deals with piracy prior to 1923, in this context referring to robbery or violence committed on the high seas.
Colonial North America at Harvard Library
Colonial North America at Harvard Library is an ambitious project that seeks to digitise Harvard’s vast collection of materials related to the North American colonies, circa the 17th and 18th centuries.
Short Teaching Module: Constantine and Christianity
Christianity is based on the teachings of Jesus of Nazareth (ca. 3 B.C.E.–29 C.E.), a Jewish religious thinker who according to Christian Scripture lived in Judaea, a province of the Roman Empire.

Constantinian Edicts
Many of the records that survive from Constantine’s reign are official edicts and proclamations, written on papyrus and parchment.