Global Contact

The League of Nations Archive
The archive offers an extensive array of primary sources that can be used in the study of global history, international relations, transnational conflict, national border creation, migration, human rights, and historical personages.
Olympic Museum
The modern Olympic Games have become a symbol of international cooperation and sportsmanship. The IOC states that the Olympics are a forum “where the world comes to compete, feel inspired, and be together."
Nobel Peace Center
However, most notable is their partnership with Minecraft Education. The Peace Center offers two Minecraft learning landscapes, Peace Builders and Active Citizen, both are targeted at students aged 8-15.
Visualizing Energy:
By combining written analysis with data visualizations, this project displays how energy policy can affect health and equity in a way that makes it interactive and easy to understand.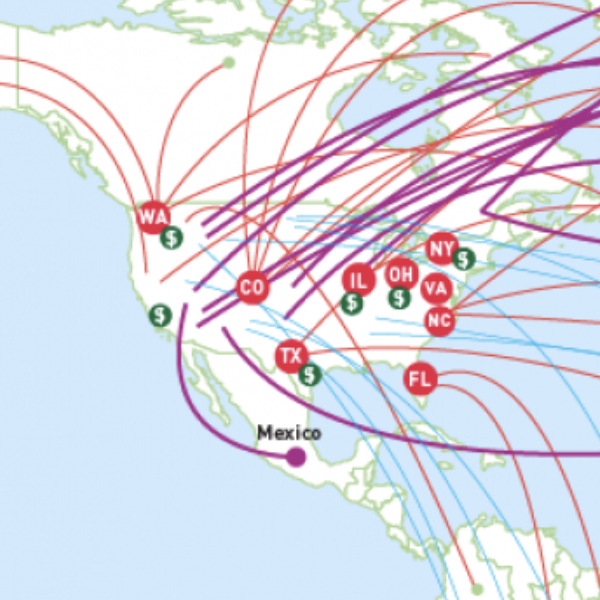
Globalizing US History
The strength of this site comes from the thorough lesson plans included in the modules. Further, the secondary and primary sources included in each would be a good classroom tool.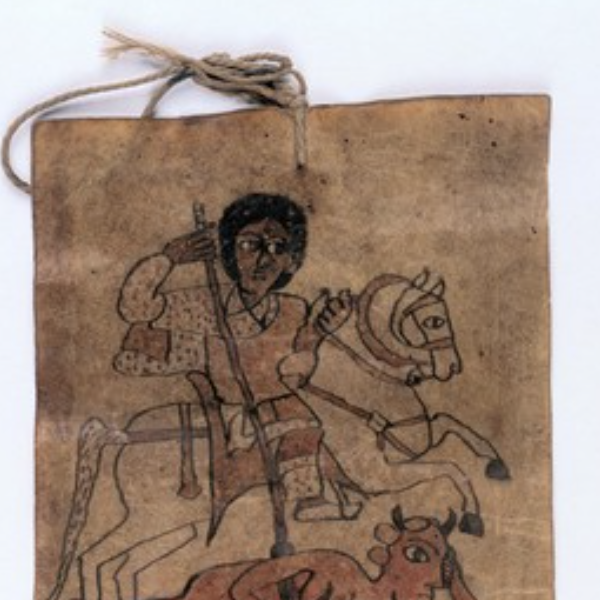
Ethiopian Healing Scrolls
Ethiopian healing scrolls are believed to eliminate sickness by ridding spirits and demons from an ill person. Originating sometime between the 1st and 8th century CE in the Axum empire, the scrolls are still used to this day, and still written in the Ge’ez script of the Axum empire.
Al-Umari’s Account of Mansa Musa’s Visit to Cairo
Mansa Musa was the leader of the Mali empire in the fourteenth century and reportedly the wealthiest person – allegedly ever. The empire covered modern-day Mali and parts of Guinea, Senegal, Mauritania, and the Gambia, and Mansa Musa expanded the territorial claim to include Gao and Timbuktu.
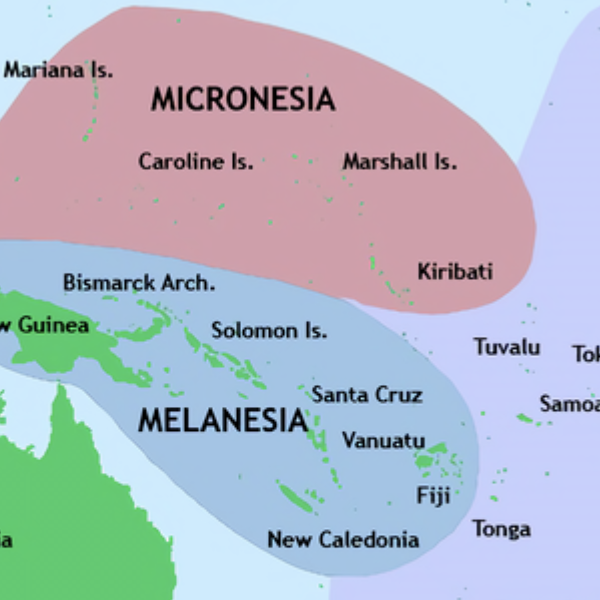
Pacific Culture Areas Map
This map illustrates the three dominant cultures in Oceania, Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia, and which islands occupy each region. This map successfully highlights the number of island nations/cultures and the overall size of Oceania.
Polynesian Oral Traditions
This collection compiled by Rawiri Taonui, a professor of Indigenous Studies, includes creation myths and stories about gods, the origin of humanity, and cultural heroes for several Polynesian cultures, such as Hawaii, Samoa, Tonga, Tahiti, and numerous others.

Moai on Easter Island
The Moai are large statues on Easter Island in Oceania, known for their distinctive head and facial features. The moai were created by the Rapa Nui people likely between 1250 and 1600 CE.