Popular Culture
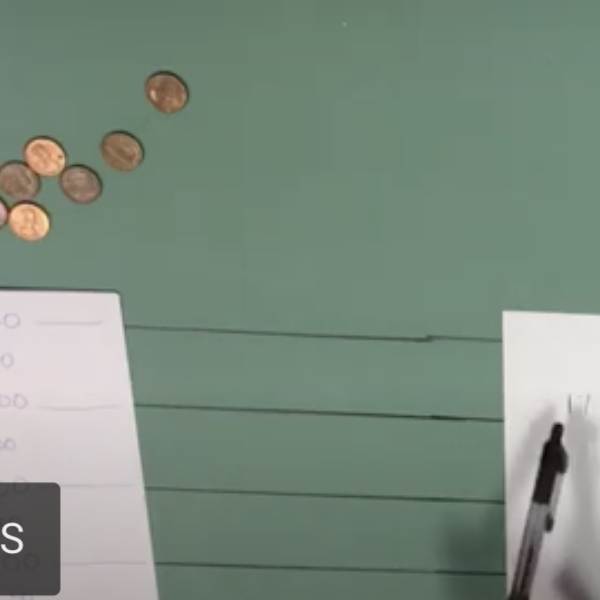

Division with an Early Modern Counting Board
Before the rise of literacy rates, counting boards such as the one featured in the video were the most common way to perform arithmetic. After pen-and-paper arithmetic replaced counting boards, Arabic numerals also became dominant throughout Europe.
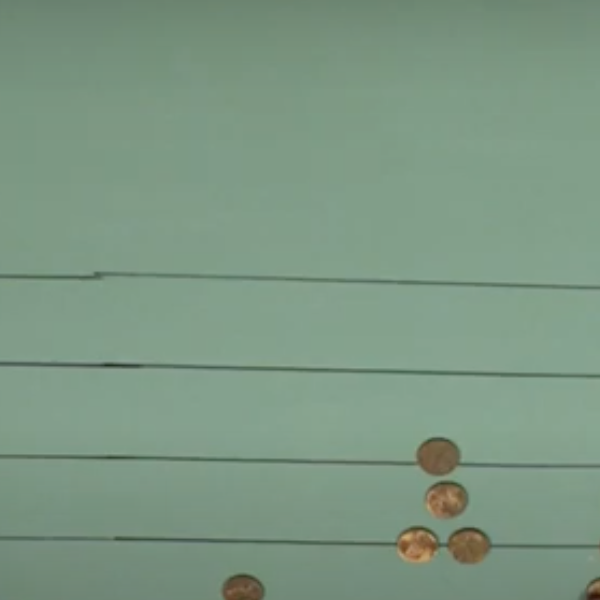

Multiplication with an Early Modern Counting Board
Before the rise of literacy rates, counting boards such as the one featured in the video were the most common way to perform arithmetic. After pen-and-paper arithmetic replaced counting boards, Arabic numerals also became dominant throughout Europe.
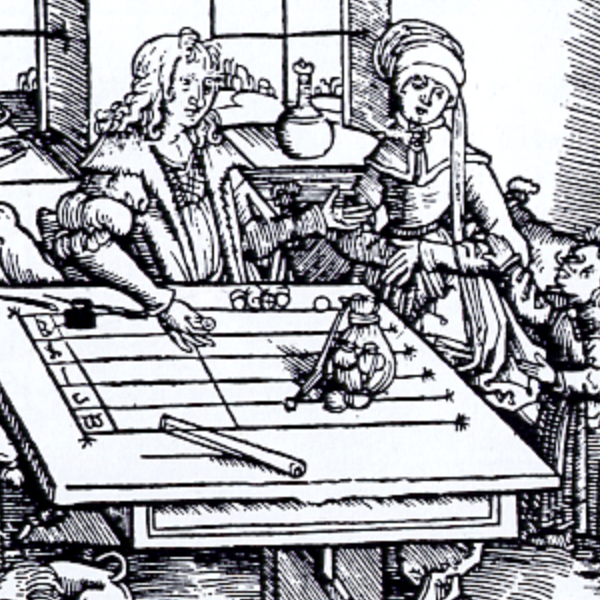

Engraving of a Rechentisch (Counting Board)
This image of an engraving depicts a man using a rechentisch, or counting board, the earliest known counting device and a precursor the abacus. The earliest known counting board is the Salamis Tablet, dating from 300 BCE, but may have been used more for gaming than for calculating.

Nok Terracotta Sculptures
Nok terracotta sculptures are the earliest-known sculptures from sub-Saharan Africa, created by the Nok culture of which little is known except their ironworking and terracotta sculptures that flourished circa 1500 BCE to 1 BCE.

Huaca Pucllana, Ancient Pyramid in Peru
Huaca Pucllana is a pyramid site built around 500 AD by the Lima culture of Peru. The pyramid was built with seven platforms made from adobe bricks and is around 82 feet (25 meters) high, and has a plaza surrounding it. The pyramid was a site of ceremonial and religious power.
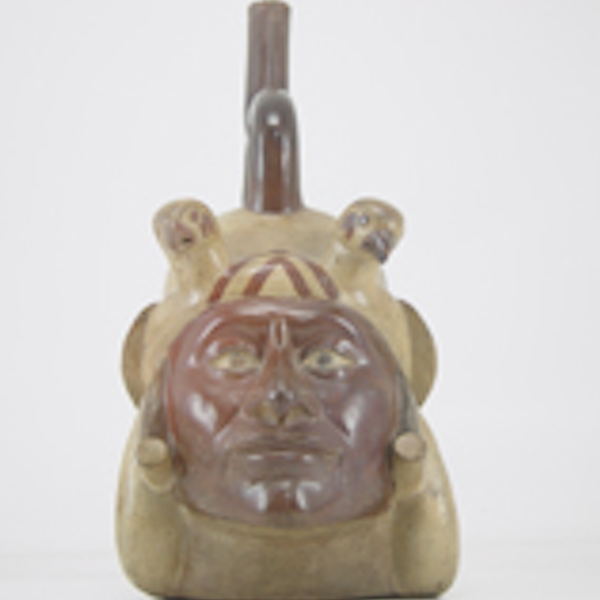

Moche Portrait Vessels
Moche portrait vessels are ceramic vessels that often featured only heads, but some also have full human bodies as well, and most are representations of adult men.

Cueva de los Manos, Rio Pinturas
Cueva de las Manos, Rio Pinturas is an archealogical site and World Heritage Site in Argentina that features cave art and rock are that dates to around 9500 to 13000 years old.
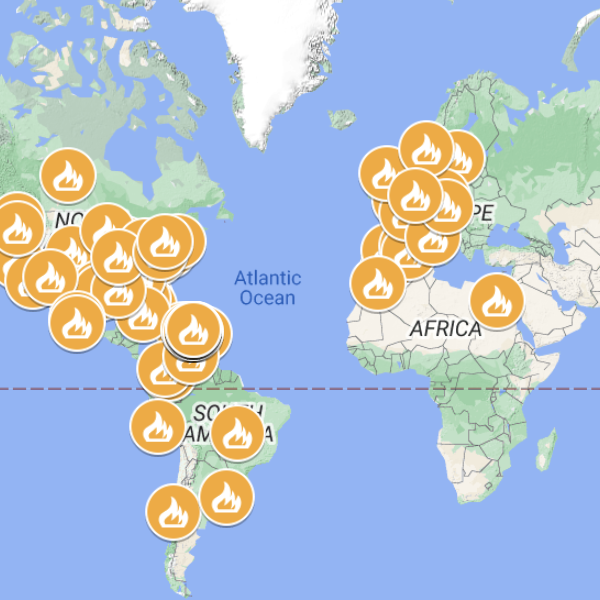
Map with Many of the Protests in Puerto Rico and the World 2019
An event in Puerto Rico that captured world attention and motivated the interest of many Puerto Ricans in the diaspora to participate was the Summer of 2019 movement.

Shell Pendant or Bead from Ecuador
This pendant or bead was made from a shell and dates back to the 3rd millennium BCE. Found in Ecuador, it was likely made by the Valdivia culture, a people who lived on the western coast and mainly subsisted off fishing and farming and flourished between the years of 3500 BCE - 1500 BCE.

Ceramic Female Figure from Ecuador
This clay figure dates from the third millennium BCE and is evidence of the earliest known ceramic traditions of any ancient peoples in the Americas. This figure, and many others like it, are from the Valdivia culture of Ecuador.